In cellular network, a cellular device used by an end user, connects to radio access network of a provider through radio signals. Cellular connectivity enables mobile communication and fixed wireless access (FWA). Internet speeds on cellular networks have improved from early GPRS (2G), and now 5G standard which promises high speeds.
Cellular devices can be of different types depending on application and functionality:
Functionality
Cellular router
Unlike a normal router which connects to the internet via cable, fiber or DSL, a cellular router uses a cellular network system. They are of two types. Bundled cellular router has an integrated modem. Modular routers on the other hand, require a separate cellular modem, which is normally linked to the router using USB Card ports.

They also have multiple LAN ethernet ports for LAN connectivity hence suitable for offices with various LAN connections, remote site connection that require multiple WAN and cellular for fallback connection, or large LAN network that may require switches and access points.
Cellular gateway
These devices allow connection of various network protocols to cellular or IP networks. They are suitable for industrial and IoT purposes which employ various sensor devices that require connectivity. They can enable WAN to RF and Ethernet to serial. They also usually appear rugged in design.

Cellular modem
This is usually a USB module that adds 4G LTE connectivity to a laptop, a computer, and sometimes a tablet. The modem may also be a PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) or a PCIe (PCI Express) that is attached to a motherboard on slot meant for cellular connection.

Cellular mobile hotspot
This is a highly portable device that converts 4G or 5G signals to Wi-Fi. The device creates WLAN network that enables multiple users within the Wi-Fi signal radius to connect to the internet. This offers better security option as opposed to public Wi-Fi.

Categories
Cellular devices can be categorized according to their applications as below.
Outdoor CPE
Outdoor cellular devices offer external applications for 4G/5G connectivity. They are usually built to withstand extreme weather conditions and rugged deployments. LAN users can connect to the outdoor CPE’s Wi-Fi if it has this option, or connect to indoor router via a LAN Ethernet port of the outdoor CPE.
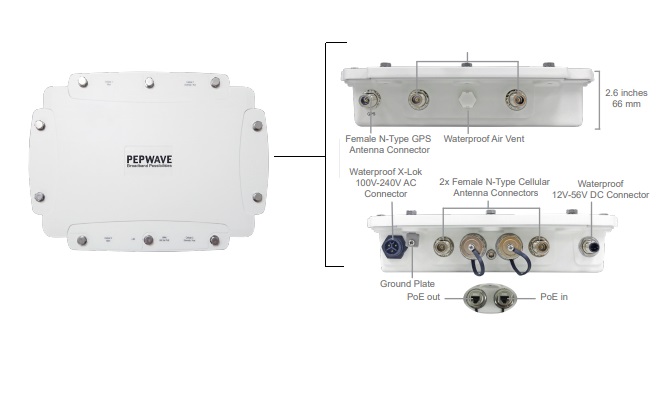
Indoor routers
These are typically used for fixed wireless access (FWA) and are suitable for home or office use. They are easy to create LAN networks via WLAN or LAN connections. For proper home or office arrangement, most routers have mounting options either on walls or inside cabinets.
Otherwise, they can also be placed on a table or any other desired place, power supply/outlet, Wi-Fi and LAN coverage considered.

Mobile routers/Portable routers
These are small sized routers that can easily be tucked into a pocket or backpack. They connect to a cellular network and gives Wi-Fi connections to multiple devices at the same time. A good portable mobile router usually has a rechargeable battery that can offer long hours of connectivity before requiring a recharge.
Ideal for road trips in RVs but may require signal improvement for areas with poor signal reception.
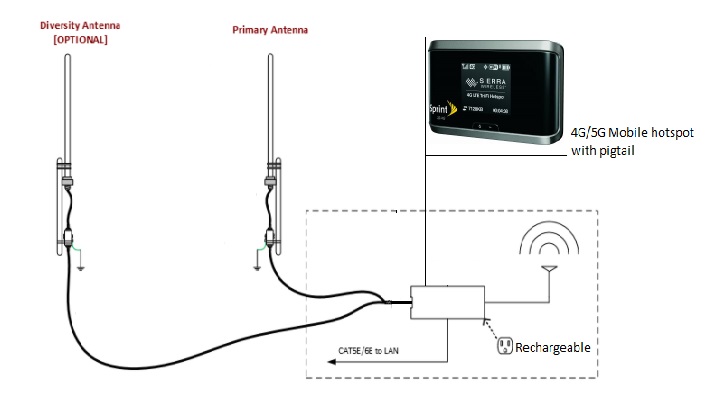
Rugged routers
Apart from outdoor cellular routers, there are routers designed for field applications such as remote site monitoring. They have rugged design such as hard casing, can tolerate vibrations and have ratings that can withstand extreme temperatures.
Due to their applications, they have various characteristics like I/O interfaces for data collection and can have multiple WAN connections for load balancing and fail-over.


